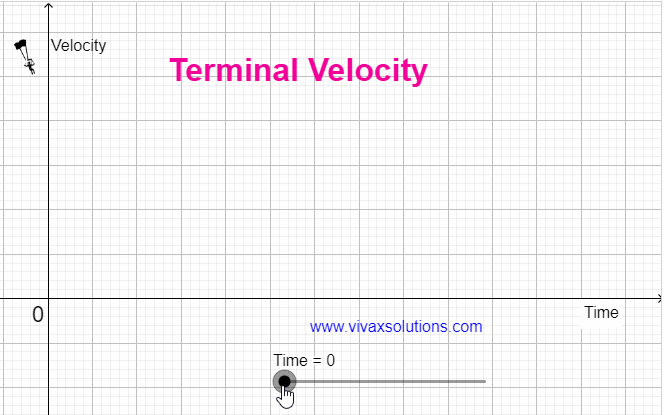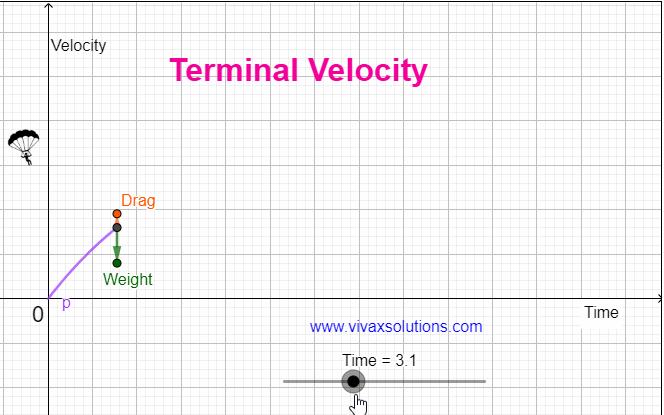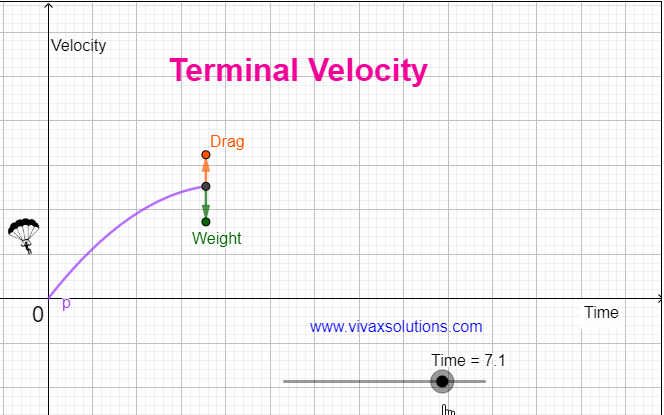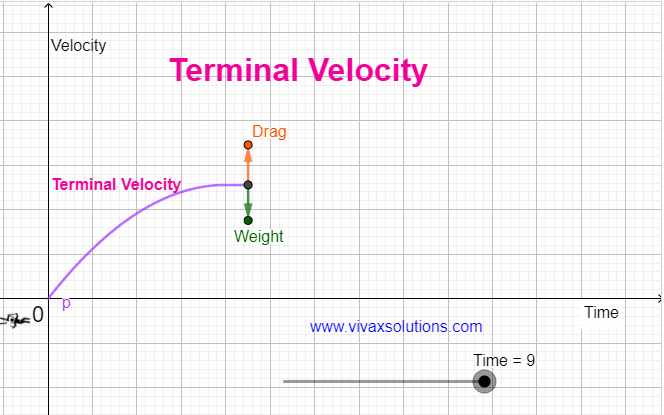
When an object comes down under gravity in the air, it is subjected at least two forces, the weight - W - and the drag / air resistance - R. The resultant force, F = W - R F = ma W - R = ma, where m and a are the mass of the object and the drag respectively. As the object comes down, the drag, goes …
Thursday, 24 February 2022
Wednesday, 23 February 2022
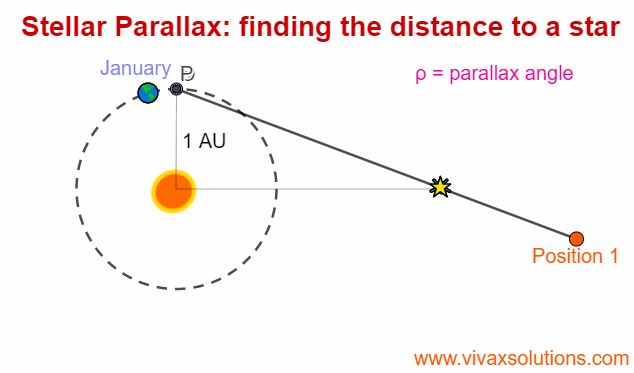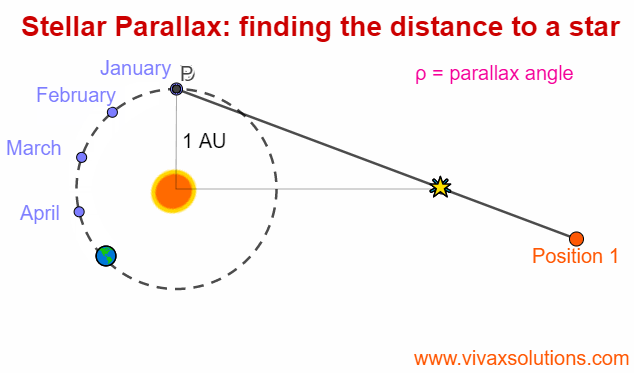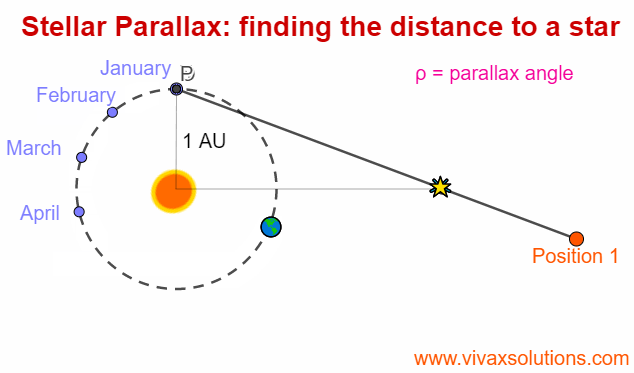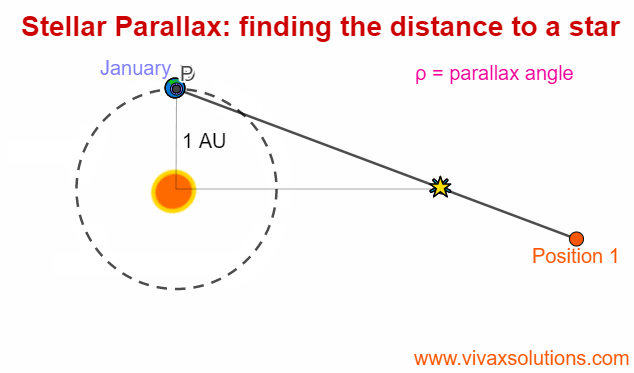
Stellar Parallax for A Level Physics - astrophysics
Parallax is an optical phenomenon when the apparent position of an an object changes with the position of the observer. In order to experience this, you can hold the your index finger some distance from your right eye - or left eye, depending on your convenience - and then moving your head slowly to…
Monday, 21 February 2022
Basic Calculus - differentiation for beginners IGCSE, AS, A-Level
The process of finding the gradient or slope of a function is the differentiation. We used to find the gradient of a straight line, just by dividing the change in 'y' by change in 'x', in a certain range of values. When it comes to a curve, however, it is not easy to find the gradien…
Saturday, 19 February 2022
Galilean Telescope
The Galilean Telescope was invented by the legendary Italian physicist, Galileo Galilei in 1609. It is a simple telescope consisting of a convex lens and a concave lens; they act as the objective and eyepiece respectively. With the aid of his invention, Galileo managed to look at J upiter’s four large…
Friday, 18 February 2022
Galileo Galilei in a Jigsaw Puzzle - interactive play
The above jigsaw puzzle is of a famous physicist who was born in the month of February. He was instrumental in turning the astronomy upside down with his discoveries and theories despite being at odds with a powerful religious establishment at that time. You can find out who he is by playing with th…
Monday, 14 February 2022
Transformation of Graphs - stretching
The tranformations of graphs are aimed at: GCSE IGCSE GCE -OL GCE - AL AS A Level High School T he above animation shows the strtching of a graph parallel to y-axis and x-axis. f(x) → af(x) is stretching parallel to y-axis by a factor a. E.g. f(x) = x² - 2x → 2f(x) = 2(x² - 2x) f(x) → f(ax) is stretching parall…
Sunday, 13 February 2022
Root-Mean-Square Voltage - r-m-s voltage of AC
The root-mean-square value of a function, f(t), is calculated as follows: Integrate the square of the function in the given range of the variable - from a to b in this case. Find the mean value of the above integral, dividing by the range of the variable - (b - a) in this case. Find the square root of…
Thursday, 10 February 2022
Transformation of Graphs - reflection
The above animation shows the reflection of graphs. It is as follows: f(x) → f(-x) is a reflection in the y-axis f(x) → -f(x) is a reflection in the x-axis E.g. f(x) = x 2 - 2x f(-x) = (-x) 2 - 2(-x) = x 2 + 2x -f(x) = -(x 2 - 2x) = - x 2 + 2x
Tuesday, 8 February 2022
Cassegrain Reflector
Cassegrain reflector consists of a concave mirror, convex mirror and an eyepiece. Parallel light from celestial objects enters
the telescope. The large concave mirror, the primary reflector, is used
to collect the light and bring it to a focus. A secondary reflector, the convex reflector, is used to…
Saturday, 5 February 2022
Transformation of Graphs - translation
f(x) → f(x + a) - a translation in the negative x-axis by a f(x) → f(x - a) - a translation in the positive x-axis by a f(x) → f(x) + a - a translation in the positive y-axis by a f(x) → f(x) - a - a translation in the negative y-axis by a E.g.1 Sketch y = x 2 + 2x - 3 and find the following: The line o…
Friday, 4 February 2022
Phase Difference between Two Points on a Wave and Path Difference Explained - interactive
In the above animation, five points on the wave are considered for the explanation. The fully interactive applet is given below for you to practise. The phase of a point implies its direction of vibration on a wave. For example, both points A and E vibrate exactly the same way are said to be in phas…
Wednesday, 2 February 2022
Terrestrial Telescope - refracting telescope explained with interactive animation
The above animation is a terrestrial telescope, a refracting telescope. It has evolved from another refracting telescope, the astronomical telescope that produces an inverted image, making it not suitable for viewing objects on the Earth. The terrestrial telescope has addressed the issue to some ext…
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)
Popular Posts
-
Multiple Choice Questions - A Level Physics and Mechanics - Time: 40 minutes Created and Programmed by Vivax Solutions St...
-
In the above animation, five points on the wave are considered for the explanation. The fully interactive applet is given below for you ...
-
Multiple Choice Questions - A Level Physics - electricity - Time: 40 minutes Created and Programmed by Vivax Solutions Star...
-
Denary to Binary Conversion Denary to binary conversion is a fundamental concept in computer science and digital electronics. It involves t...
-
Multiple Choice Questions - A Level Physics - Capacitors - Master capacitor concepts with this interactive A Level Physics quiz! Whether...
TOP CATEGORIES
- a level computer science (11)
- a level physics (43)
- gcse maths (30)
- gcse physics (14)
- general physics (11)
Featured Post
Labels
a level computer science
(11)
A Level Maths
(27)
a level physics
(43)
featured
(4)
GCSE Computer Science
(9)
gcse maths
(30)
gcse physics
(14)
general physics
(11)
math
(2)
physics
(2)
Blog Archive
-
▼
2022
(77)
-
▼
February
(12)
- Terminal Velocity - A Level Physics
- Stellar Parallax for A Level Physics - astrophysics
- Basic Calculus - differentiation for beginners IGC...
- Galilean Telescope
- Galileo Galilei in a Jigsaw Puzzle - interactive play
- Transformation of Graphs - stretching
- Root-Mean-Square Voltage - r-m-s voltage of AC
- Transformation of Graphs - reflection
- Cassegrain Reflector
- Transformation of Graphs - translation
- Phase Difference between Two Points on a Wave and ...
- Terrestrial Telescope - refracting telescope expla...
-
▼
February
(12)