 |
| Root-Mean-Square Voltage in the UK |
The root-mean-square value of a function, f(t), is calculated as follows:
- Integrate the square of the function in the given range of the variable - from a to b in this case.
- Find the mean value of the above integral, dividing by the range of the variable - (b - a) in this case.
- Find the square root of the value that you get in step 2).
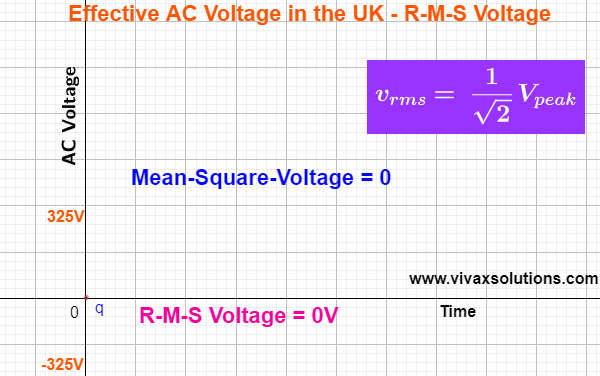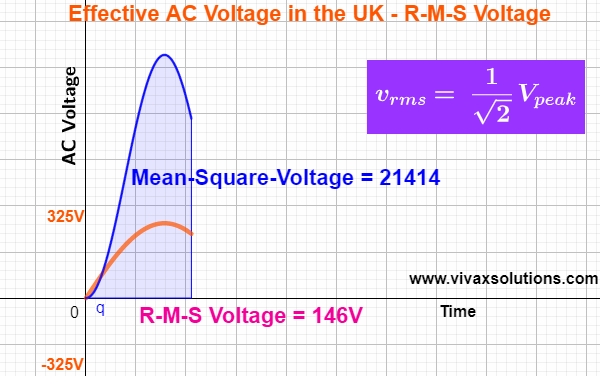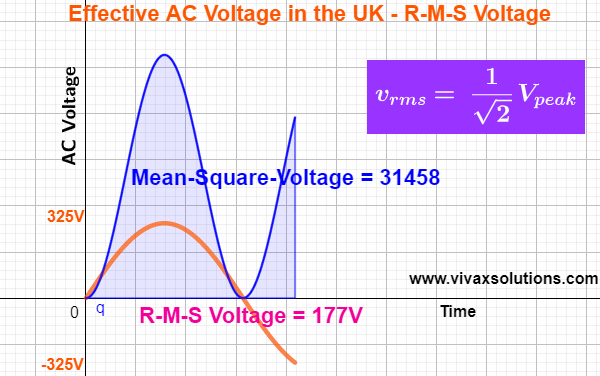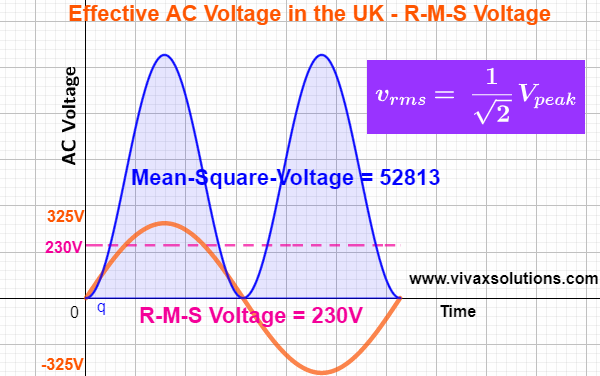
The AC voltage is a sine curve and it changes with time as follows:
v = 325 sin(t), where the peak value in the UK is about 325V.
The calculation is as follows:
The r.m.s value of the AC gives the same power given by
an equal DC through the same resistor.
E.g.
If the resistor in question is 5Ω, peak voltage and r-m-s voltage are
325V and 230V respectively,
Power = V2/R
Power = 2302/5, not 3252/5, which is the same as under 230V, DC through 5Ω resistor.
For interactive practise, here is the applet:

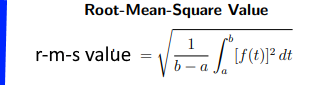
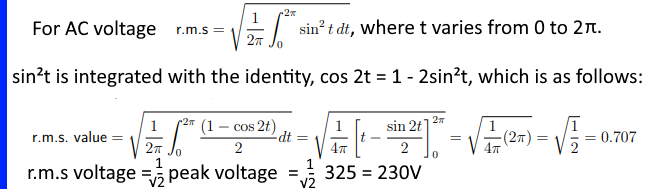




0 comments:
Post a Comment