Concave functions
If f''(x) ≤ 0 in a given interval of x, the function is said to be concave.
Convex functions
If f''(x) ≥ 0 in a given interval of x, the function is said to be convex.
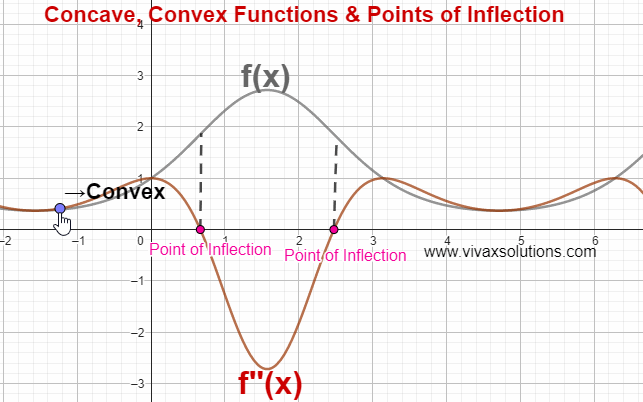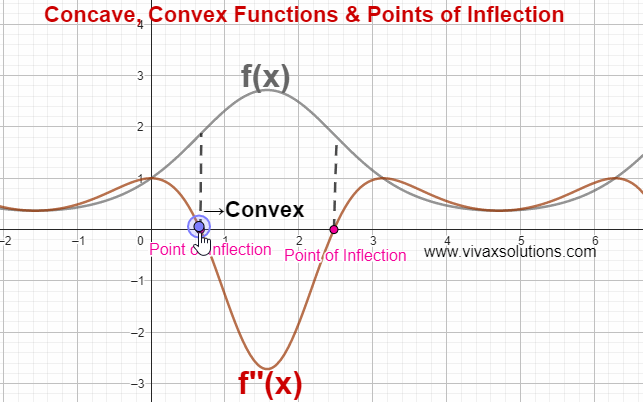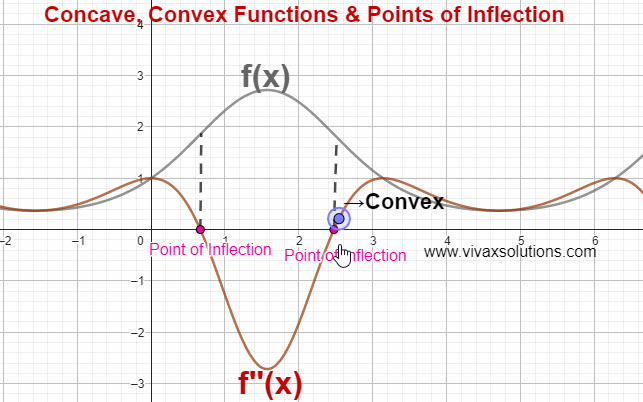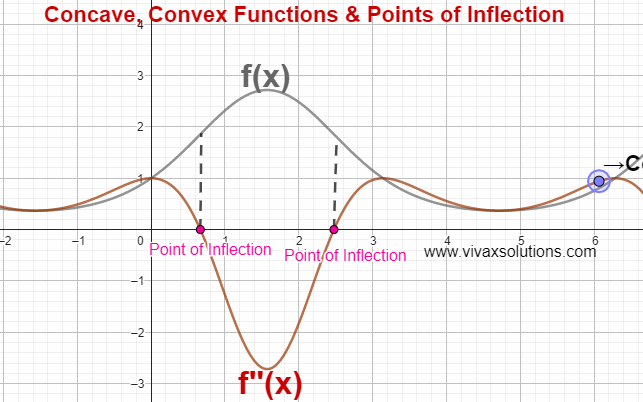
Point of Inflection
The point at which a curve changes being concave to convex or vice versa is called a point of inflection.
E.g.
f(x) = x3 - 2x² + 5x - 4
f'(x) = 3x² - 4x + 5
f''(x) = 6x - 4
At the point of inflection,
f''(x) = 0
6x - 4 = 0
x = 2/3 = 0.67
There is a point of inflection at x = 0.67.
If x = 0.6
f''(0.6) = 3.6 - 4 = -0.4
f''(0.6) < 0 - the function is concave.
If x = 0.8
f''(0.8) = 4.8 - 4 = 0.8
f''(0.8) > 0 - the function is convex.
In the above simulation, there are two points of inflection. The simulation can be practised interactively here; just move the point gently to see the change.
Points of inflection on the Bell Curve - Normal Distribution
There are two points of inflection on the bell curve. You can practise the following simulation interactively to understand it.





0 comments:
Post a Comment