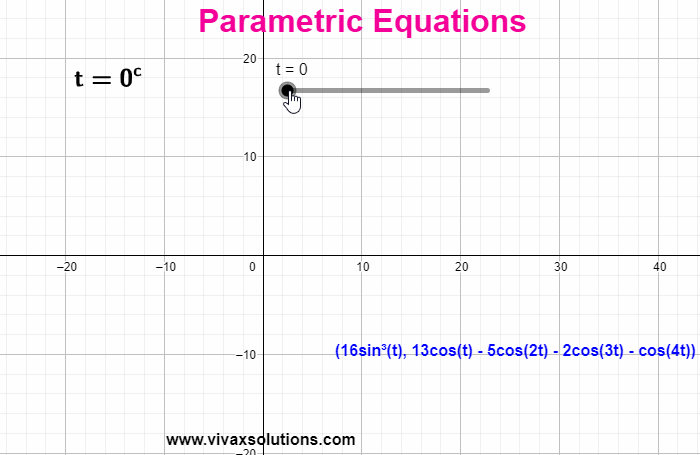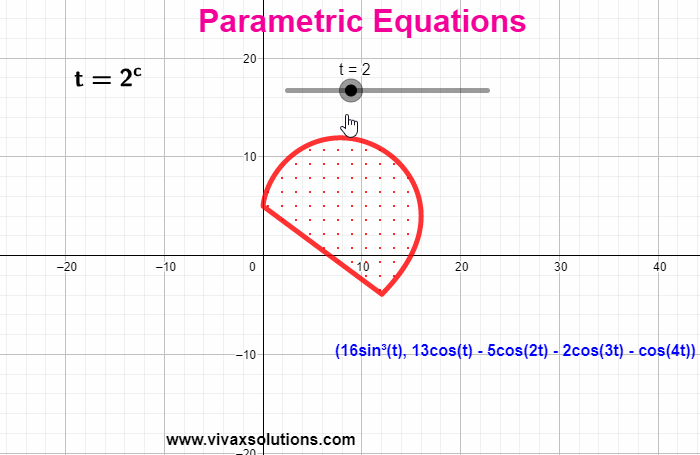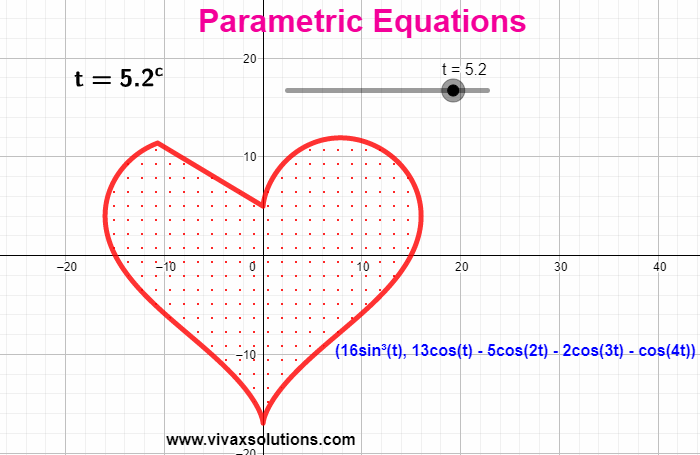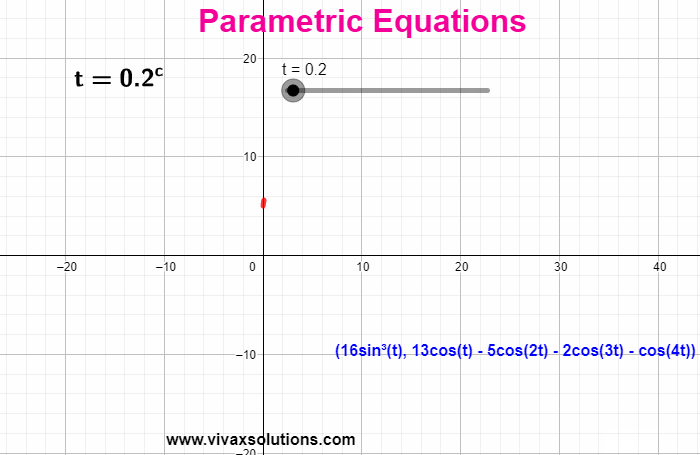
When the coordinates of a function are expressed in terms of a third independent variable, parametric equations are produced. E.g. x = 3 sin (t) | y = 3 cos (t) - t is the parameter
sin t = x/3 => sin 2 t = x 2 /9
cos t = y/3 => cos 2 t = y 2 /9
x 2 + y 2 = 9
x 2 + y 2 = 3 2
This is a circle with radius…
Sunday, 27 March 2022
Wednesday, 23 March 2022
Circle Theorem Challenges for GCSE, IGCSE, GCE OL
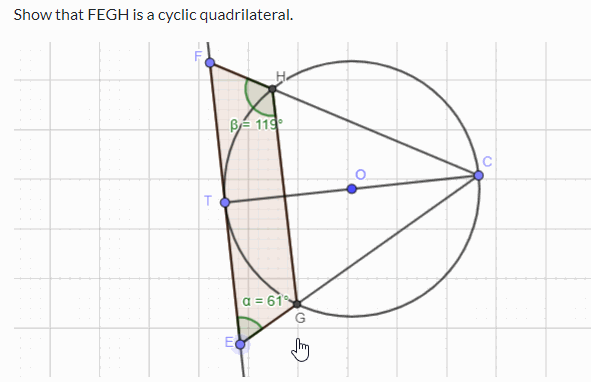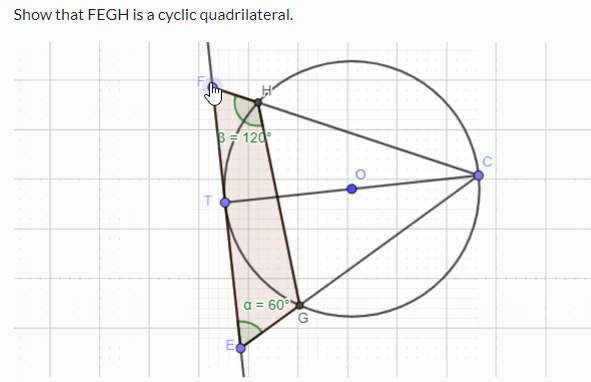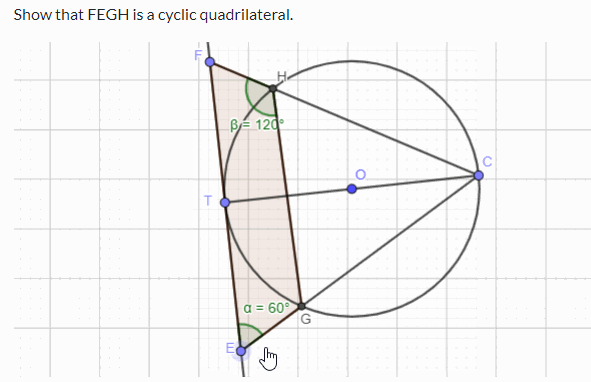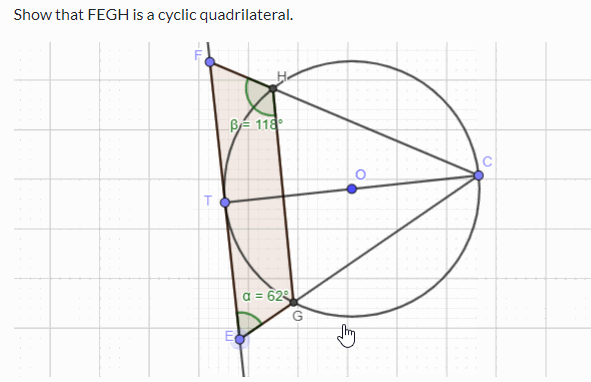
Challenge Prove that FEGH in the following simulation is a cyclic quadrilateral. You can use the circle theorems and geometry to prove the above. If you want to practise circle theorems with interactive simulations and learn through worked examples, please visit this page .
Tuesday, 22 March 2022
Polygon Simulator for maths: year 9, GCSE, IGCSE and GCE OL
Polygons A closed shape with many sides is a polygon. Sum of Interior Angles If the number of sides is n and the sum of interior angles is T, T = (n-2)180 The table, given below, shows how the sum of interior angles varies with the number of sides. Sum of Exterior Angles The sum of exterior angles is 360 0 …
Monday, 21 March 2022
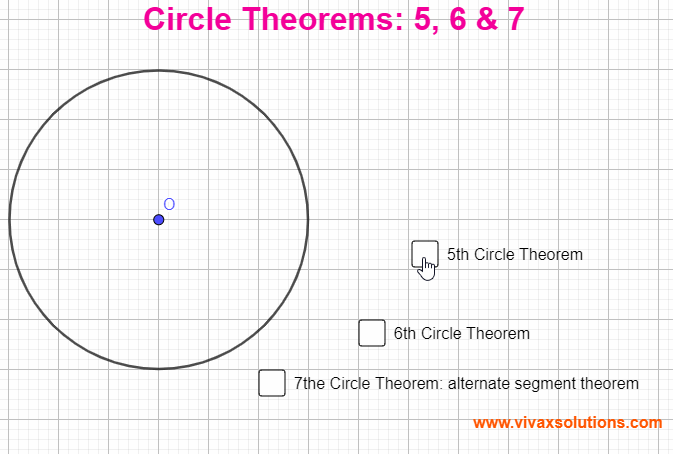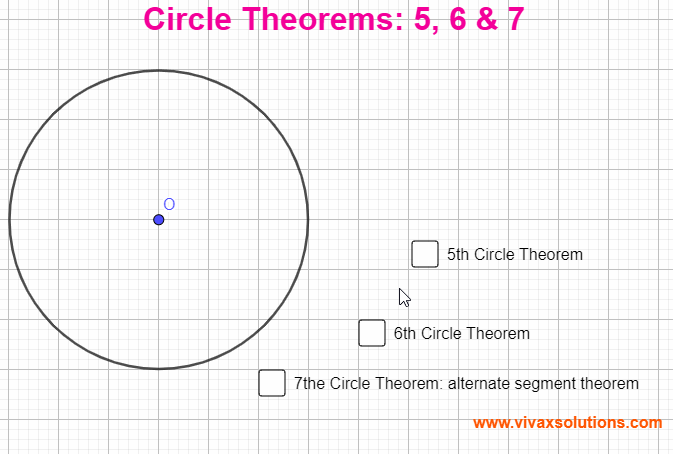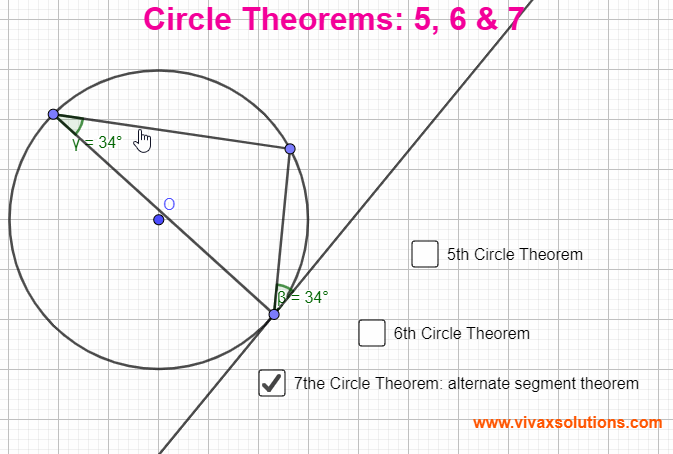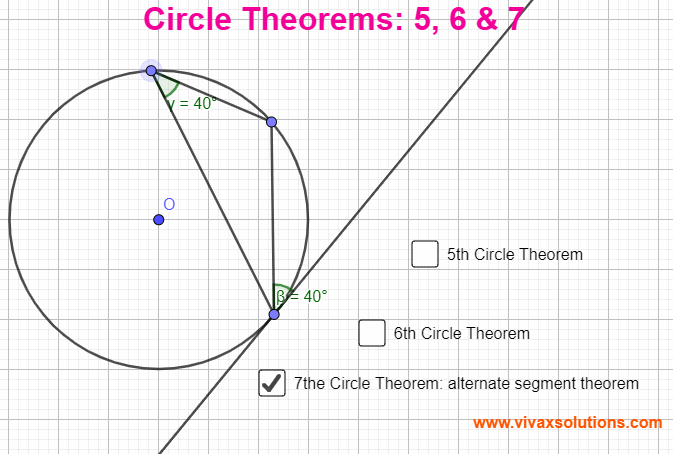
Circle Theorems 5, 6 & 7 for GCSE, IGCSE and GCE OL
Circle Theorems Circle Theorem 5 The angle between a radius and the tangent at the point of contact is a right angle. Circle Theorem 6 Two tangents drawn from a point to a circle are equal in length. Circle Theorem 7 The angle between a chord and a tangent is equal to the angle in the alternate segment. You…
Saturday, 19 March 2022
The Diffraction Grating for A Level Physics
Diffraction grating is a glass slide with a series of parallel transparent lines, called slits, on it. When a beam of monochromatic beam strikes it, light waves diffract through the slits, creating a pattern of alternating bright and dark spots, known as fringes, on a surface where light falls - in a…
Friday, 18 March 2022
Fourth Circle Theorem: Cycling Quadrilaterals - GCSE, IGCSE, GCE OL
Cyclic Quadrilaterals A quadrilateral whose vertices touch a circle is called a cyclic quadrilateral. Fourth Circle Theorem The opposite angles of a cyclic quadrilateral add up to 1800. You can practise it interactively with the following applet:
Thursday, 17 March 2022
First three circle theorems for GCSE, IGCSE and GCE OL
The above simulations show the first three circle theorems. You can practise them interactively with the following simulation: If you want more interactive circle theorem simulations and worked examples, please click here .
Wednesday, 16 March 2022
The net of a cube: for Year 9, GCSE & IGCSE maths
The above simulation shows how a cube is formed from a net or vice a versa. The net of a triangular-based prism is as follows: In the GCSE or IGCSE exams, students are often asked to draw a net of a regular solid object such as a prism, cube or even a tetrahedron for which the former are required to …
Tuesday, 15 March 2022
Maximizing the power of load in an electric circuit
Let the EMF, internal resistance, load and the current of a circuit be E, r, R and I respectively. E = I(R + r) I = E/(R + r) The power of the load, the external resistor in this case, is as follows: P = VI P = E 2 R/(R + r) 2
Let's differentiate P with respect to R
dP/dR = E 2/ / (R + r) 2 - 2E 2 R / (R +…
Monday, 14 March 2022
Conservation of Mechanical Energy: potential and kinetic energy
Conservation of Mechanical Energy The sum of the kinetic energy and potential energy of an object that moves under gravity remains constant throughout its journey. Kinetic Energy(KE) The energy possessed by a moving object is called Kinetic energy. If the mass and the velocity of an object are m and v …
Sunday, 13 March 2022
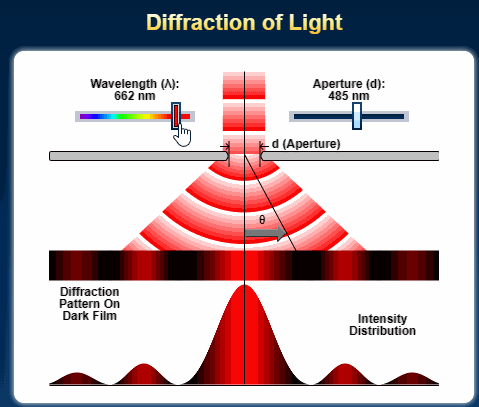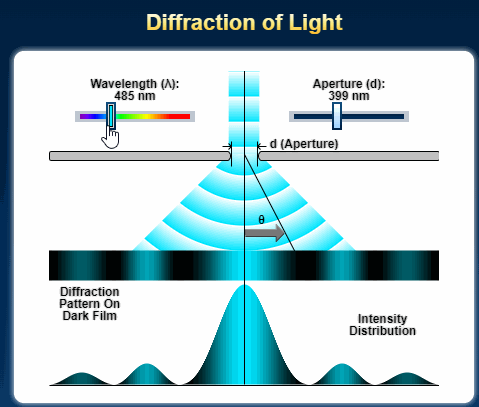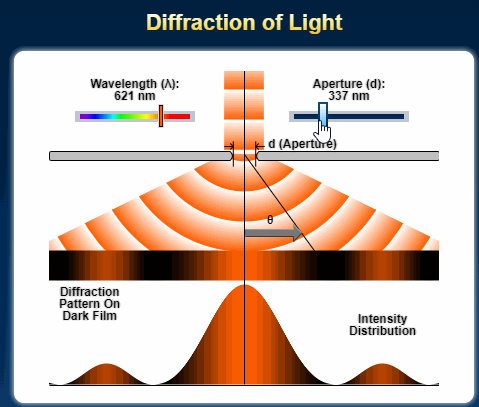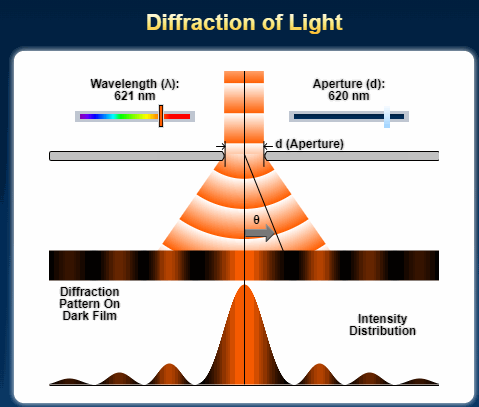
Single Slit Diffraction for A Level Physics
The diffraction of a beam of light through a single slit is given by the following equation. x = d sin θ, where x is the path difference and θ is the deviation of the path as an angle. d is the width of the slit or aperture. The greater the angle of diffraction, the greater the value of x. If x is a …
Modelling with Parametric Equations: A Level Pure Mathematics
Modelling with Parametric Equations for A Level pure mathematics Parametric equations can be used to model real life situations. For example, the above animation shows how the path of a boat in river can be modelled by parametric equations. The boat sails from west to east and the river flows from no…
Saturday, 12 March 2022
Measuring the Speed of Light: Michelson's Method
In 1926, Albert Michelson, the German-born American physicist, came up with a method to measure the speed of light to a high degree of accuracy despite the technology not being advanced enough at that time. In recognition of his achievement in the field of science, he was awarded the Nobel Prize for…
Thursday, 10 March 2022
Python Algorithms for Computer Science - Euclid Algorithm
Euclid's Algorithm is one of the oldest algorithms known to mankind. It was found in Euclid's Elements, something that dates back to 300 B.C. When Euclid came up with the algorithm, mathematics was not known as it is today; in fact, he used geometrical methods in his discovery, as algebra w…
Wednesday, 9 March 2022
Instantaneous Velocity
The instantaneous velocity of an object can be found by the gradient of the displacement/time graph at a given time. E.g. In the above graph, which you can practise interactively below, the gradient, when the time, t = 1s, is as follows: v = (3 - 0)/(1 - 0) = 3 m/s You can practise the calculations in…
Tuesday, 8 March 2022
Histograms Simulator: GCSE, IGCSE, AS, A Level, IB, GCE O L and A L
A histogram represents continuous grouped data as a running total in each group. The area of a each bar, as opposed to the height of each bar, represents the frequency of each group or bar. The greater the area, the greater the frequency. Since classes are not of equal width, as this is the case in a …
Monday, 7 March 2022
Refraction of Light - simulator for GCSE, IGCSE, A Level, IB, GCE O Level, GCE A Level
Refraction When light moves from a medium to another medium, its speed and the direction changes. This is called refraction of light. Snell's Law When light refracts, the ratio of the sine of the angle of incidence to the ratio of the sine of the angle of refraction remains the same for any two gi…
Sunday, 6 March 2022
Frequency Amplitude and Wavelength of a Transverse Wave - simulation
Waves A wave carries energy from a point to another point in a medium / vacuum without the movement of the particles along with it. In the above animation, the wave moves from the left to the right; the particles, however, just vibrate vertically without moving along with the wave. Transverse Waves If …
Saturday, 5 March 2022
Constructing an Inscribed Circle: for GCSE, IGCSE and GCE O-Level
Inscribed Circle A circle that touches the three sides of a triangle from inside is called an inscribed circle. In order to construct an inscribed circle, Construct the angular bisector of each angle Note the point where the three angular bisectors intersect at Use the point in step 2, as the centre, us…
Friday, 4 March 2022
Constructions and Loci for GCSE and IGCSE Maths; circumcircle
A circle that touches the vertices of a tringle from outside is called a circumcircle. In order to construct it, the following simple steps can be followed in order: Construct the three perpendicular lines of each side. Find the point where the lines in step 1 intersect. Using the point in step 2) as …
Thursday, 3 March 2022
Perpendicular Lines - for GCSE, IGCSE, O Level & AS
If two lines are perpendicular, the gradient of one line is the negative reciprocal of the other line. E.g.1 Find the equation of the perpendicular line to the equation, y = 2x - 3 that goes through the point (4,5). The gradient of the perpendicular line = -1/2 = -0.5 For the perpendicular line, m = -0.5…
Measuring the distance to stars for A Level physics - parsec
When it comes to distances involved in the objects in space, three major units are used. They are, astronomical unit light-year parsec Astronomical unit - AU This is the average distance between the Sun and the Earth. 1AU = 150 million km = 1.5 x 10 11 m The astronomical unit, AU, is used to express the d…
Wednesday, 2 March 2022
Total resistance of combined resistors - series and parallel circuits
Resistors can be combined in two different methods; they are in series and in parallel. If two resistors, R 1 and R 2 2 , are in series, the total resistance, R t , is given by the following formula. R t = R 1 + R 2 If the same resistors are in parallel, the total resistance is as follows: R t = 1/R 1 + 1/R 2 E.g. …
Tuesday, 1 March 2022
Finding area under curves by integration
The area under a curve and the x-axis can be found by integrating the curve between two chosen values of x. Area = ∫ x 2 /4 dx E.g.
Area under the curve between x = 1 and x = 4 = ∫ x 2 /4 dx
= [x 3 /12] 4 1
= 64/12 - 1/12
= 63/12
= 5.3(1 d.p.)
For interactive practice of the above, here is the appl…
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)
Popular Posts
-
Multiple Choice Questions - A Level Physics and Mechanics - Time: 40 minutes Created and Programmed by Vivax Solutions St...
-
In the above animation, five points on the wave are considered for the explanation. The fully interactive applet is given below for you ...
-
Multiple Choice Questions - A Level Physics - electricity - Time: 40 minutes Created and Programmed by Vivax Solutions Star...
-
Denary to Binary Conversion Denary to binary conversion is a fundamental concept in computer science and digital electronics. It involves t...
-
Multiple Choice Questions - A Level Physics - Capacitors - Master capacitor concepts with this interactive A Level Physics quiz! Whether...
TOP CATEGORIES
- a level computer science (11)
- a level physics (43)
- gcse maths (30)
- gcse physics (14)
- general physics (11)
Featured Post
Labels
a level computer science
(11)
A Level Maths
(27)
a level physics
(43)
featured
(4)
GCSE Computer Science
(9)
gcse maths
(30)
gcse physics
(14)
general physics
(11)
math
(2)
physics
(2)
Blog Archive
-
▼
2022
(77)
-
▼
March
(25)
- Mathematicians love parametric equations!
- Circle Theorem Challenges for GCSE, IGCSE, GCE OL
- Polygon Simulator for maths: year 9, GCSE, IGCSE a...
- Circle Theorems 5, 6 & 7 for GCSE, IGCSE and GCE OL
- The Diffraction Grating for A Level Physics
- Fourth Circle Theorem: Cycling Quadrilaterals - GC...
- First three circle theorems for GCSE, IGCSE and GC...
- The net of a cube: for Year 9, GCSE & IGCSE maths
- Maximizing the power of load in an electric circuit
- Conservation of Mechanical Energy: potential and k...
- Single Slit Diffraction for A Level Physics
- Modelling with Parametric Equations: A Level Pure ...
- Measuring the Speed of Light: Michelson's Method
- Python Algorithms for Computer Science - Euclid Al...
- Instantaneous Velocity
- Histograms Simulator: GCSE, IGCSE, AS, A Level, IB...
- Refraction of Light - simulator for GCSE, IGCSE, A...
- Frequency Amplitude and Wavelength of a Transverse...
- Constructing an Inscribed Circle: for GCSE, IGCSE ...
- Constructions and Loci for GCSE and IGCSE Maths; c...
- Perpendicular Lines - for GCSE, IGCSE, O Level & AS
- Measuring the distance to stars for A Level physic...
- Total resistance of combined resistors - series an...
- Finding area under curves by integration
- Resistance of a rectangular block
-
▼
March
(25)